An Ethanolic extract from a shark having potent anti-angiogenic activity: its anti-angiogenic mechanism and clinical application
An Ethanolic extract from a shark having potent anti-angiogenic activity: its anti-angiogenic mechanism and clinical application
Abstract
An ethanol extract from shark muscle has been shown to have potent angiogenic activity when mixed together with olive oil in a ratio of 1part extract to 9 parts olive oil. This mixture has been given the trade name SuperMaco (SMO).
The anti-angiogenic activity was evident in both in vitro and in vivo studies in rats. When combined with the known angiogenic stimulatory growth factors Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), Platelet Derived Growth Factor (PDGF), Transforming Growth Factor-Beta ( TGF-β) and Fibroblast Growth Factor -2 (FGF-2), SMO completely eliminated the stimulation induced by these growth factors. Possible mechanisms for this activity are that SMO is competing for receptor sites on the endothelial cell surface by preferential binding to those sites or by binding to the growth factors themselves. Studies were conducted using soluble forms of VEGF-R1 and VEGF-R2 and it was found that SMO inhibited complex formation of the VEGF with both receptors. This inhibitory effect by SMO was enhanced when SMO was pre-incubated with VEGF receptors.
In another study, the effect of SMO on VEGF receptor phosphorylation using human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and a human breast carcinoma cell line (MDA-MB-231) was investigated. The in vitro cell proliferation assay indicated that SMO reversed the increase in VEGF promoted cell proliferation in both HUVEC and MDA-MB-231 cells. Using Western Blot analysis it was observed that SMO significantly inhibited VEGF promoted VEGF receptor-1 , VEGF receptor-2 and tyrosine phosphorylation in HUVEC and MDA-MB-231 cells in a dose related manner. These results suggest that SMO appears to block the binding of VEGF with the receptors and inhibit the signal transduction pathways.
-
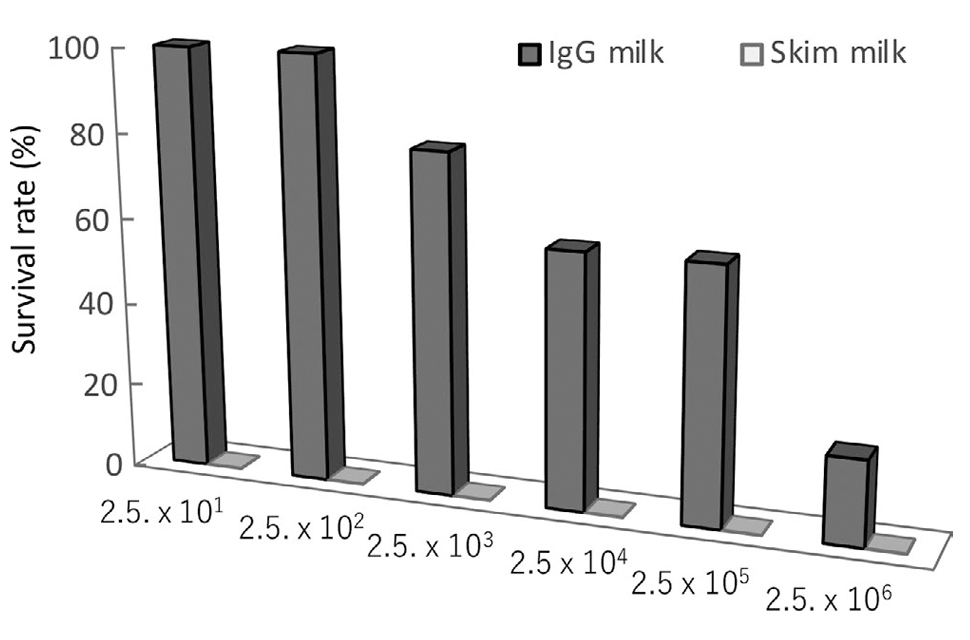 Enriched bovine IgG fraction prevents infections with Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis, and Mycobacterium avium
Enriched bovine IgG fraction prevents infections with Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis, and Mycobacterium avium
-
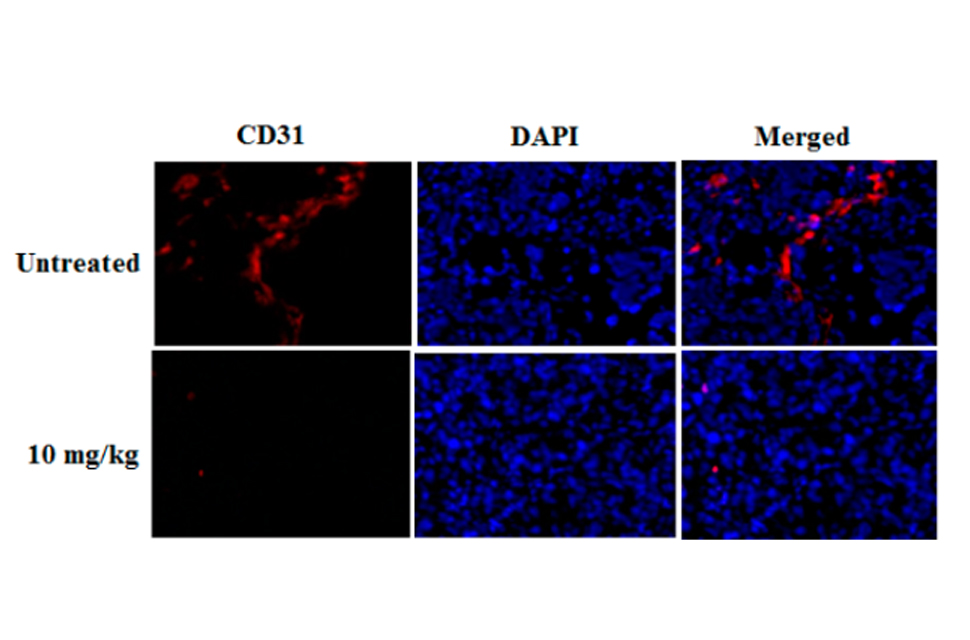 New Natural Pigment Fraction Isolated from Saw Palmetto: Potential for Adjuvant Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
New Natural Pigment Fraction Isolated from Saw Palmetto: Potential for Adjuvant Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
 Red pigment from Saw palmetto: A natural product for potential alternative cancer treatment
Red pigment from Saw palmetto: A natural product for potential alternative cancer treatment
-
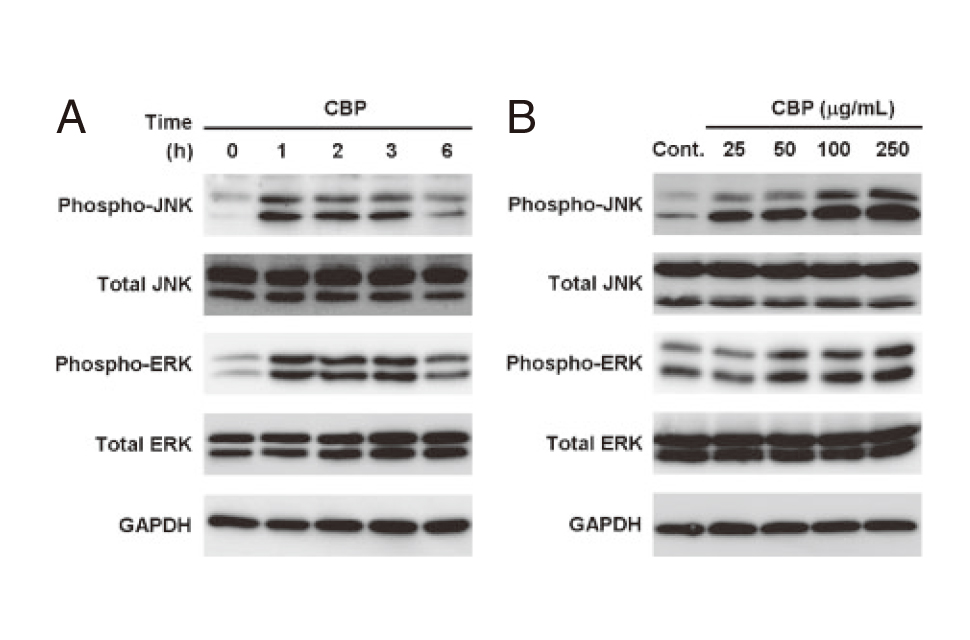 CBP Facilitate Osteogenesis through Activation of the JNK-ATF4 Pathway
CBP Facilitate Osteogenesis through Activation of the JNK-ATF4 Pathway
-
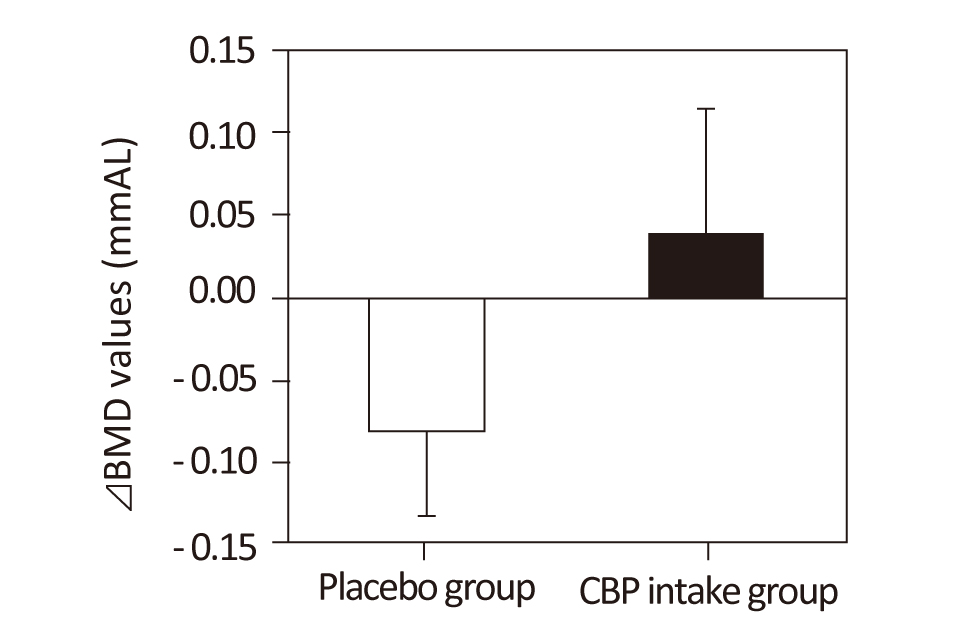 Concentrated-Bovine protein (CBP) increases Bone Mineral Density
Concentrated-Bovine protein (CBP) increases Bone Mineral Density
-
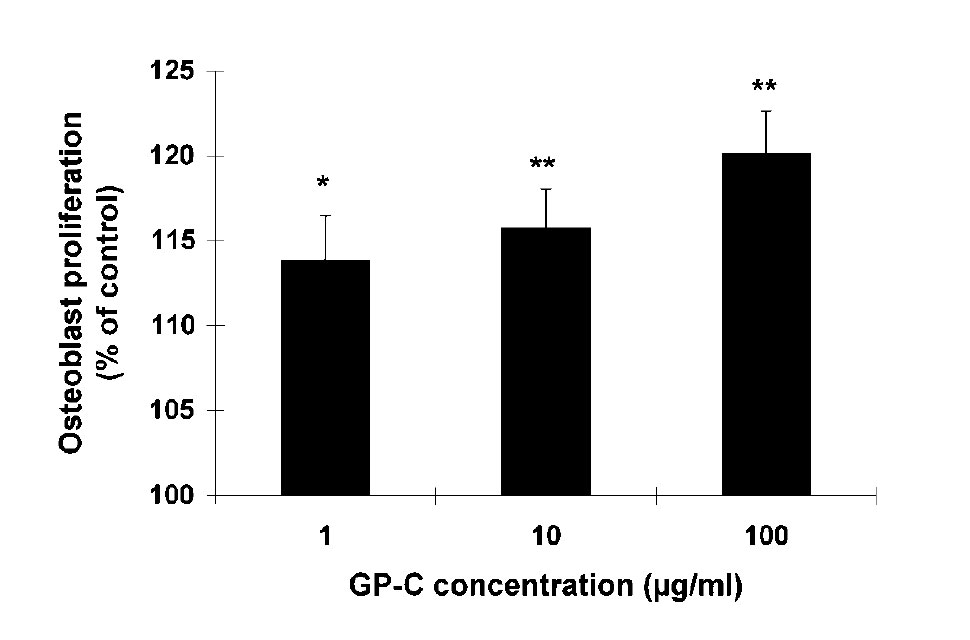 Effect of a Growth Protein-Colostrum Fraction on Bone Development in Juvenile Rats
Effect of a Growth Protein-Colostrum Fraction on Bone Development in Juvenile Rats
-
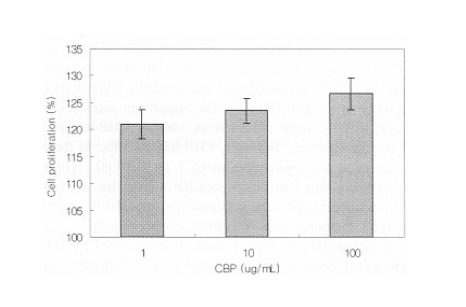 Effects of Colostrum Basic Protein from Colostrum Whey Protein: Increased in Osteoblast Proliferation and Bone Metabolism
Effects of Colostrum Basic Protein from Colostrum Whey Protein: Increased in Osteoblast Proliferation and Bone Metabolism
-
 An Ethanolic extract from a shark having potent anti-angiogenic activity: its anti-angiogenic mechanism and clinical application
An Ethanolic extract from a shark having potent anti-angiogenic activity: its anti-angiogenic mechanism and clinical application
-
 Shark Lipids for Treatment of Malignant Diseases
Shark Lipids for Treatment of Malignant Diseases
-
 Inhibition of Cancer Growth and Metastases by Preparations Based on Shark Oil
Inhibition of Cancer Growth and Metastases by Preparations Based on Shark Oil
-
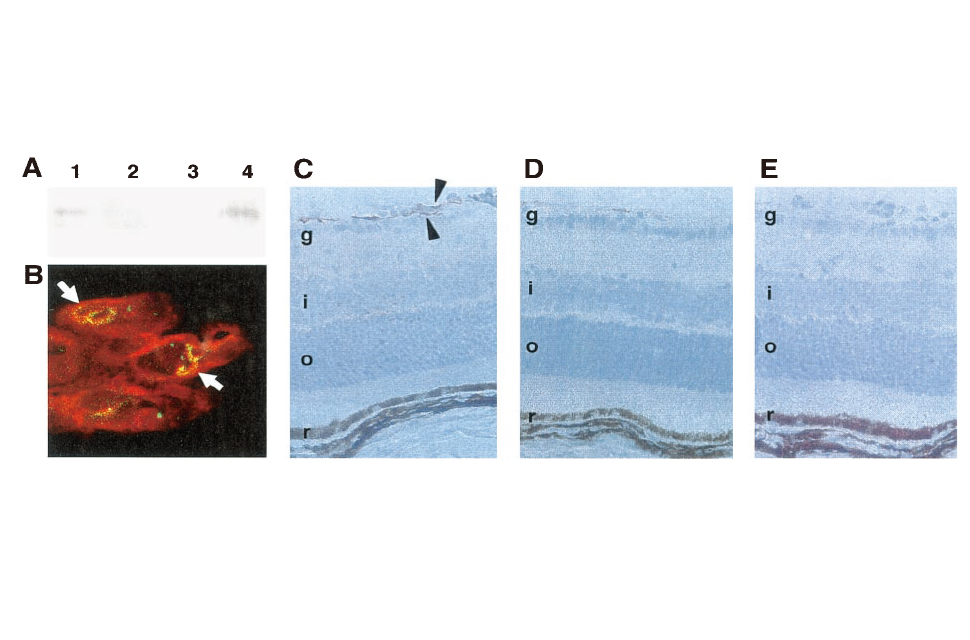 Leptin Stimulates Ischemia-Induced Retinal Neovascularization
Leptin Stimulates Ischemia-Induced Retinal Neovascularization
-
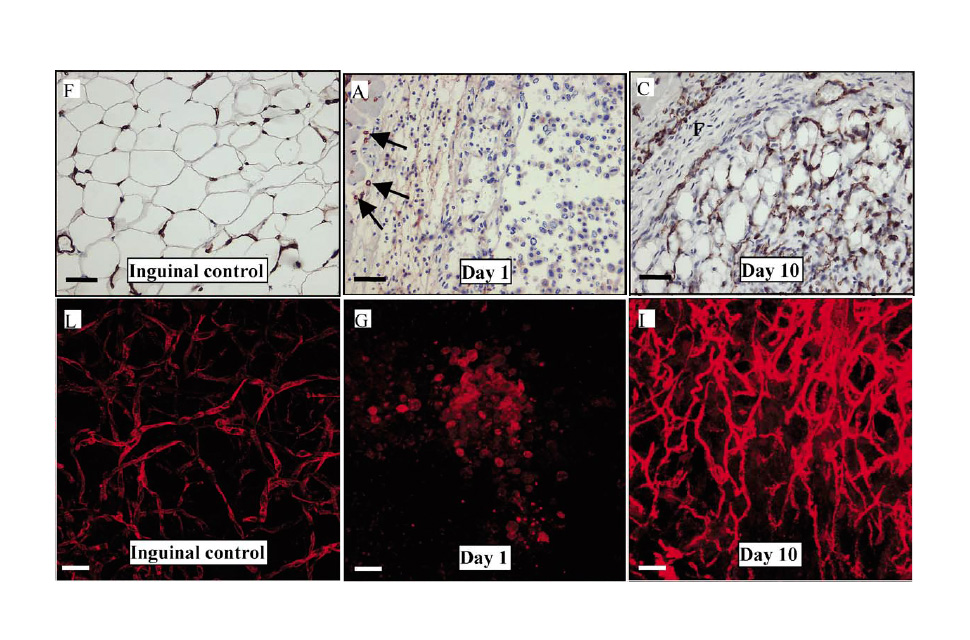 Angiogenesis in an in vivo model of adipose tissue development
Angiogenesis in an in vivo model of adipose tissue development
-
 The effects of functional foods, such as Agaricus, Pleurotus cornucopiae (Paulet) Rolland var. citrinopileatus (Sing.) Ohira. , Hericium erinaceum, Arabinoxylan, Shark cartilage and Shark extracted lipid on growth of implanted Mouse LM8 Dunn osteosarcoma
The effects of functional foods, such as Agaricus, Pleurotus cornucopiae (Paulet) Rolland var. citrinopileatus (Sing.) Ohira. , Hericium erinaceum, Arabinoxylan, Shark cartilage and Shark extracted lipid on growth of implanted Mouse LM8 Dunn osteosarcoma
-
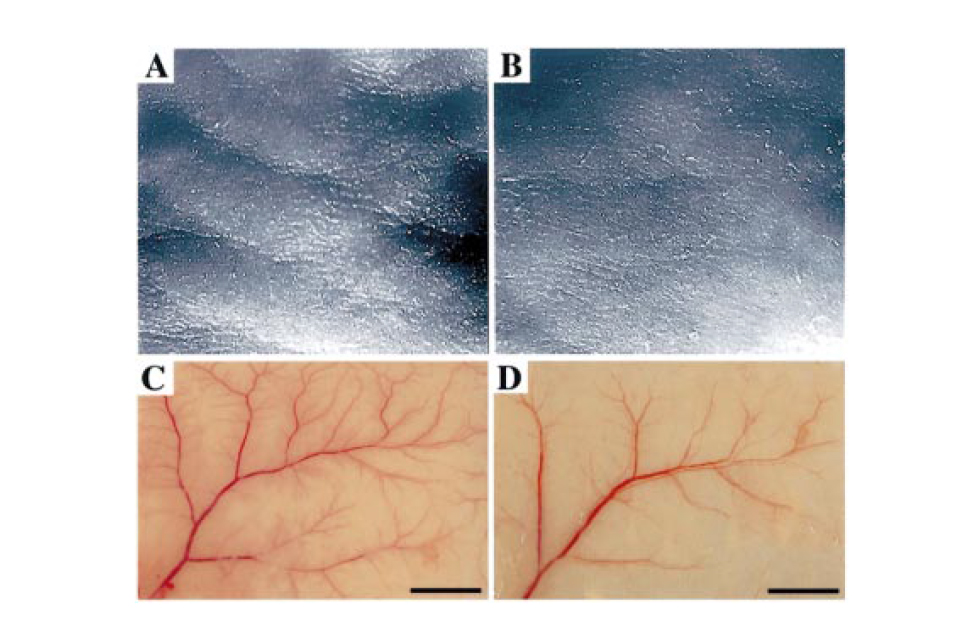 Targeted Overexpression of the Angiogenesis Inhibitor Thrombospondin-1 in the Epidermis of Transgenic Mice Prevents Ultraviolet-B-Induced Angiogenesis and Cutaneous Photo-Damage
Targeted Overexpression of the Angiogenesis Inhibitor Thrombospondin-1 in the Epidermis of Transgenic Mice Prevents Ultraviolet-B-Induced Angiogenesis and Cutaneous Photo-Damage


